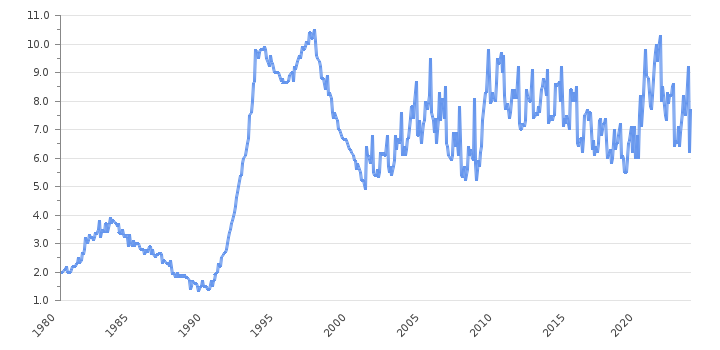
In February 2025, Sweden’s labor market exhibited notable dynamics. The unemployment rate stood at 9.4%, a decrease from January’s 10.4%. This decline suggests a potential stabilization following the previous month’s surge. Sweden’s unemployment rate analysis in February 2025 stood at 9.4%, with youth unemployment at 28.1%, highlighting ongoing labor market challenges.
Sweden’s Unemployment Rate Rate Analysis Trends
Comparing year-over-year data, February’s unemployment rate increased from 8.5% in 2024 to 9.4% in 2025. This rise indicates underlying challenges in the labor market.
Labor Force Statistics
The number of unemployed individuals reached 533,000 in February, up by 53,000 compared to the same month last year. Conversely, employment declined by 16,000, totaling 5.16 million. The employment rate fell by 0.4 percentage points to 67.7%.
Youth Unemployment
Youth unemployment remains a concern. The rate for individuals aged 15-24 was 28.1% in February. This high percentage underscores the need for targeted interventions to integrate young people into the workforce.
Seasonally Adjusted Figures
Seasonally adjusted data shows a slight improvement. The unemployment rate decreased to 8.9% in February from 9.7% in January. This suggests that the January spike may have been an anomaly.
Labor Force Participation
The labor force participation rate grew by 0.2 percentage points to 74.7%. This increase indicates more individuals are either employed or actively seeking employment.
Hours Worked
The average total number of hours worked per week amounted to 170.5 million. This metric provides insight into the overall workload and economic activity.
Gender Disparities
Gender disparities persist in unemployment rates. Female unemployment was 8.9% in 2024, slightly higher than male unemployment at 8.3%. Addressing these disparities is crucial for equitable labor market development.
Comparative Analysis
Sweden’s unemployment rate is higher than some European counterparts. For instance, Germany reported a rate of 3.5% in September 2024. This comparison highlights the need for Sweden to evaluate and potentially reform its labor policies.
Economic Implications
A high unemployment rate can strain public finances due to increased welfare expenditures. It may also dampen consumer spending, affecting economic growth. Policymakers must consider these factors when designing economic strategies.
Policy Responses
To combat rising unemployment, Sweden could implement several measures:
- Job Creation Programs: Investing in infrastructure and green energy projects to generate employment.
- Skill Development: Offering training programs to equip workers with skills in high-demand sectors.
- Youth Employment Initiatives: Providing incentives for companies to hire young workers, such as tax breaks or subsidies.
Long-Term Outlook
Addressing structural issues in the labor market is essential for sustainable employment. This includes:
- Education System Reforms: Aligning curricula with market needs to ensure graduates possess relevant skills.
- Labor Market Flexibility: Balancing worker protections with the need for businesses to adapt to changing economic conditions.
- Innovation Promotion: Encouraging entrepreneurship and the growth of emerging industries to create new job opportunities.
Conclusion
While the decrease in the unemployment rate from January to February 2025 is a positive sign, the year-over-year increase indicates ongoing challenges. Targeted policies focusing on job creation, skill development, and youth employment are vital. By addressing these issues, Sweden can work towards a more robust and inclusive labor market.