Rare Earth Elements (REEs) are essential to modern life, yet their extraction and sourcing remain complex and challenging. While these elements power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles and renewable energy, many people don’t realize how difficult they are to obtain. In this guide, we’ll uncover where REEs are found, the mining techniques used to extract them, and the environmental and geopolitical challenges involved. By the end, you’ll have a deeper understanding of why REEs are so valuable and why their supply remains a critical global concern.
Where Are Rare Earth Elements Found?
REEs are more abundant in the Earth’s crust than their name suggests, but they are rarely found in high concentrations. Instead of being mined as single elements, they are usually mixed with other minerals, making extraction complicated and expensive.
Major REE Deposits Around the World
REEs are distributed globally, but only a few countries have economically viable deposits. Here are the key locations:
1. China (The REE Giant)
China dominates REE production, accounting for about 69% of global mining and 85% of refining. The Bayan Obo mine in Inner Mongolia is the world’s largest REE deposit, supplying elements like neodymium and dysprosium used in high-tech industries.
2. United States (Reviving Domestic Mining)
The Mountain Pass mine in California is the largest rare earth mine in the U.S. It was once a major supplier but declined in the 1990s due to environmental regulations and China’s lower production costs. Efforts are now underway to rebuild domestic supply chains and reduce reliance on China.
3. Australia (A Key Alternative Source)
Australia is one of the fastest-growing REE producers, with the Lynas Corporation operating the Mount Weld mine. The country is actively investing in expanding its rare earth processing capacity to compete globally.
4. Canada (Untapped Potential)
Canada has large REE reserves, particularly in Quebec and the Northwest Territories. Companies are exploring ways to develop sustainable mining operations that could reduce dependence on China.
5. Brazil and India (Emerging Players)
Both Brazil and India have substantial REE deposits. Brazil’s reserves are largely untapped, while India is focusing on increasing domestic production to support its growing technology sector.
6. Africa (A Hidden Resource)
Africa has promising REE reserves, with nations like South Africa, Burundi, and Malawi holding significant deposits. However, infrastructure and investment challenges have slowed development.

How Are REEs Mined?
Extracting REEs is a complicated process that involves multiple steps, from mining to separation and refining. Let’s break down the methods used:
1. Open-Pit Mining (The Most Common Method)
Most REE mining is done through open-pit methods, where large sections of land are excavated to access rare earth-rich ores. This method is efficient but has significant environmental consequences, including habitat destruction and toxic waste.
2. In-Situ Leaching (A Cleaner Alternative)
Some REE deposits, particularly in China, are extracted using in-situ leaching. This process involves injecting chemicals into the ground to dissolve rare earth minerals, which are then pumped to the surface. While less disruptive to the landscape, it poses risks of groundwater contamination.
3. Monazite and Bastnäsite Processing
REEs are typically extracted from two main minerals:
- Monazite: Contains thorium, making it radioactive and harder to process.
- Bastnäsite: Found in large deposits like those in Bayan Obo and Mountain Pass, it is easier to refine but still requires complex separation techniques.
4. Refining and Separation
Once mined, REEs must be chemically separated, which is incredibly challenging due to their similar properties. This requires multiple rounds of solvent extraction, a costly and time-consuming process. China’s dominance in refining has been a key factor in controlling the global supply chain.
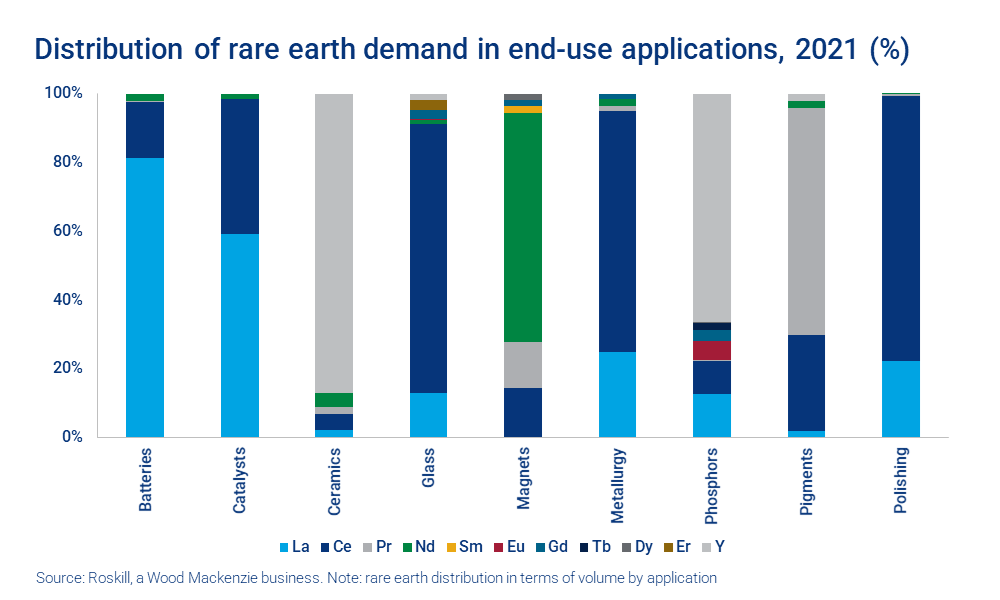
The Challenges of Sourcing Rare Earth Elements
1. Environmental Concerns
REE mining generates toxic waste, including radioactive by products. Many mines, especially in China, have been criticized for their environmental impact. Countries are now pushing for cleaner, more sustainable methods.
2. Geopolitical Tensions and Supply Chain Risks
With China controlling most of the refining process, many nations are vulnerable to supply disruptions. Trade disputes and export restrictions have raised concerns about securing stable sources.
3. High Costs and Investment Barriers
REE mining requires massive financial investment. Developing new mines takes years, and refining is expensive. This makes it difficult for new players to enter the market.
4. The Need for Recycling and Sustainability
Recycling REEs from electronic waste is a growing industry. While still in its early stages, improving recycling could reduce the need for new mining operations and minimize environmental harm.
Conclusion
As global demand for REEs continues to grow, countries and companies are searching for solutions to make mining cleaner, more efficient, and less dependent on China. Governments are investing in research, developing alternative sources, and expanding domestic refining capabilities.
Mattias Knutsson, an expert in Global Procurement and Business Development, emphasizes the urgency of diversifying REE supply chains. According to Knutsson, industries must adopt long-term strategies to reduce dependency on a single country while investing in sustainable mining and recycling technologies. His insights suggest that securing rare earth elements is not just about economics but also about global stability and innovation.
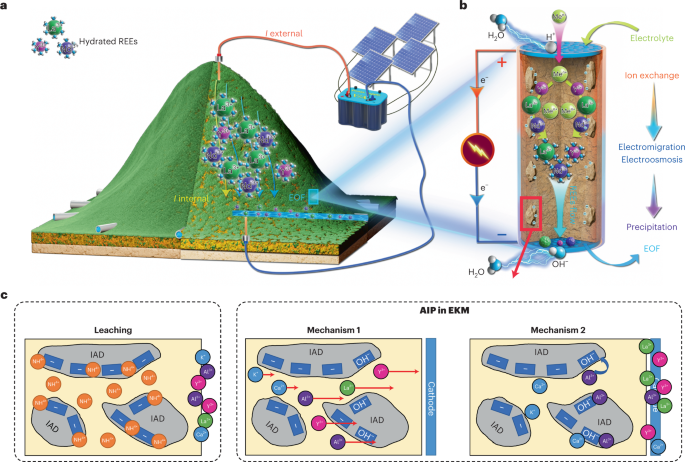
Stay Tuned for More on REEs!
In the next part of our REE series, we’ll dive into the Global Supply Chain and China’s Dominance, uncovering the strategies different countries are using to break free from dependence on China. You won’t want to miss it!
Get ready to explore the power dynamics of REEs and what they mean for the future of technology and international trade!
👉 Continue reading to the next part to learn how the global supply chain shapes the rare earth industry!
REEs Previous Posts you might also like:
Chapter 1: