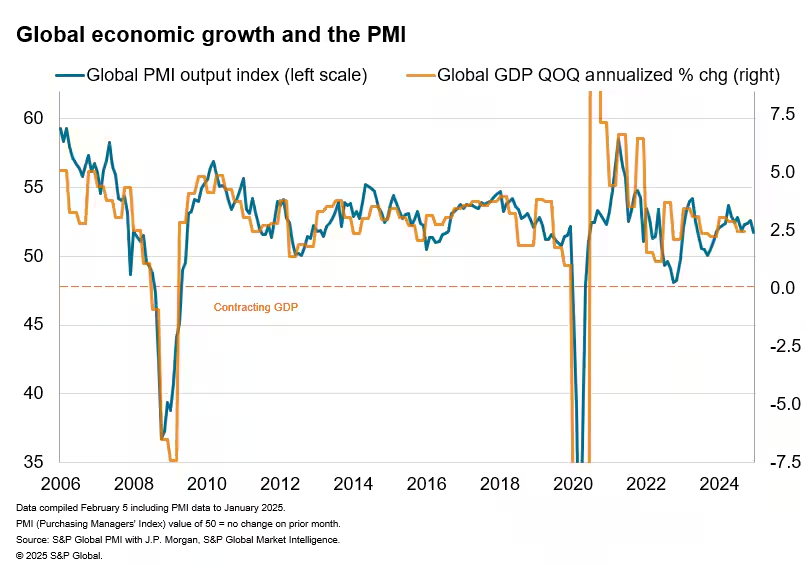
In February 2025, the global manufacturing sector displayed modest growth, continuing its expansion for the second consecutive month. The J.P.Morgan Global Manufacturing PMI, compiled by S&P Global, registered 50.1, slightly up from 49.6 in January. A reading above 50 indicates expansion, while below 50 signifies contraction.
PMI Report: February 2025 Regional Insights
- China: China’s manufacturing activity reached a three-month high in February, with the official PMI rising to 50.2 from 49.1 in January. This improvement suggests that recent stimulus measures may be stabilizing the economy. However, ongoing trade tensions with the U.S., including newly announced tariffs, cast uncertainty over the sustainability of this recovery.
- United States: The S&P Global U.S. Manufacturing PMI increased to 51.6 in February from 51.2 in January, indicating a second consecutive month of expansion. This growth is attributed to rising domestic sales and improved business confidence following recent political developments.
- Eurozone: The Eurozone’s manufacturing sector continued to face challenges, with PMI readings remaining below the neutral 50 mark. Germany and France, two of the region’s largest economies, reported PMIs of 46.1 and 45.5, respectively, suggesting ongoing contractions.
- India: India maintained its position as one of the strongest performers, with its manufacturing sector experiencing robust growth. Specific PMI figures for February were not available at the time of this report.
Key Indicators
- Output and New Orders: Global manufacturing output and new orders experienced slight growth, with indices at 50.6 and 50.8, respectively. This suggests a marginal increase in production and demand.
- Employment: Employment levels continued to contract, with the employment index at 48.5. While some regions, like the U.S., saw increased hiring, significant job cuts in China, the Eurozone, and the UK offset these gains.
- Prices: Input cost inflation accelerated to a five-month high, leading to a steeper rise in selling prices. This trend reflects increased cost pressures across both manufacturing and service sectors.

Global Economic Context
The modest expansion in global manufacturing comes amid various economic challenges. Trade tensions, particularly between the U.S. and China, have introduced uncertainties. The U.S. administration announced an additional 10% tariff on Chinese goods, effective March 4, exacerbating existing strains. China’s policymakers are expected to unveil fresh stimulus measures at the upcoming annual parliamentary meeting to counteract these external pressures and support domestic demand.
In the Eurozone, persistent contractions in manufacturing highlight structural issues and potential vulnerabilities to global trade dynamics. Conversely, India’s continued robust performance underscores the resilience of its domestic market and effective policy measures.
Outlook
While the global manufacturing sector shows signs of stabilization, the path ahead remains uncertain. Inflationary pressures, geopolitical tensions, and potential supply chain disruptions pose risks to sustained growth. Businesses and policymakers must remain vigilant, adapting strategies to navigate this complex landscape. Upcoming economic data releases and policy announcements will provide further insights into the trajectory of global manufacturing in the coming months.





